As modern IT environments become increasingly complex, traditional operations and monitoring approaches are struggling to keep up.
Cloud-native architectures, microservices, distributed systems, hybrid and multi-cloud deployments generate massive volumes of data every second. Logs, metrics, traces, events, and alerts flood operations teams, making it difficult to detect issues early, identify root causes, and resolve incidents quickly.
This is where AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) comes into play.
AIOps leverages machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics to automate and enhance IT operations.
Instead of relying solely on rule-based alerts and manual troubleshooting, AIOps platforms analyse vast amounts of operational data in real time to detect anomalies, predict incidents, reduce noise, and enable faster resolution.
In this blog, we’ll explore what AIOps is, why it matters, how it works, its core components, use cases, tools, benefits, challenges, and how organisations can successfully adopt AIOps in their DevOps and SRE practices.
What is AIOps?
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) refers to the use of AI and ML techniques to automate, optimise, and improve IT operations processes.
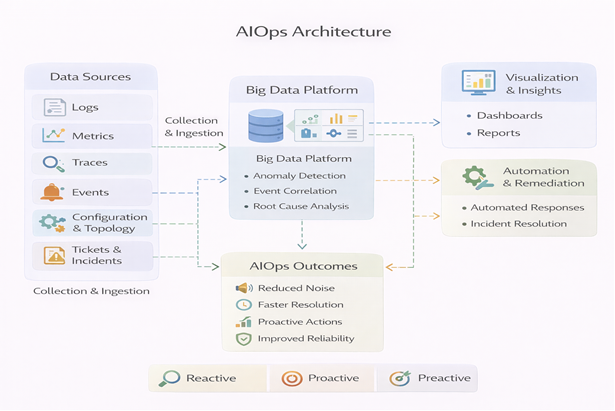
AIOps platforms ingest data from multiple sources, such as:
- Logs
- Metrics
- Events
- Traces
- Configuration data
- Topology data
- Alerts
Using advanced analytics, AIOps systems correlate this data to:
- Detect anomalies
- Reduce alert noise
- Identify root causes
- Predict future issues
- Automate remediation
In short, AIOps turns raw operational data into actionable intelligence.
Why AIOps is Important
Traditional IT operations rely heavily on:
- Static thresholds
- Manual alert triage
- Reactive incident management
- Siloed monitoring tools
These approaches fail in modern environments because:
- Systems are highly dynamic
- Microservices change frequently
- Infrastructure scales automatically
- Failures are often non-deterministic
Key Challenges Without AIOps
- Alert fatigue
- Slow incident resolution
- High Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
- High Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR)
- Human error
- Poor visibility into distributed systems
How AIOps Solves These Problems
- Automates data analysis at scale
- Detects issues before users are impacted
- Correlates signals across tools and domains
- Enables proactive and predictive operations
Core Components of AIOps
AIOps platforms generally consist of the following building blocks:
1. Data Ingestion
AIOps tools collect data from diverse sources:
- Monitoring tools (Prometheus, CloudWatch)
- Logging platforms (ELK, Splunk)
- Tracing tools (Jaeger, Zipkin)
- ITSM systems
- CI/CD pipelines
- Cloud providers
2. Big Data Platform
The collected data is stored and processed using scalable big data technologies that can handle high volume, velocity, and variety.
3. Machine Learning Models
ML algorithms are applied to:
- Identify patterns
- Detect anomalies
- Predict failures
- Cluster-related events
4. Correlation Engine
Correlates alerts and events across systems to reduce noise and identify the root cause instead of symptoms.
5. Automation & Remediation
Integrates with automation tools to:
- Trigger scripts
- Roll back deployments
- Scale resources
- Restart services
- Open or close incidents automatically
6. Visualisation & Insights
Dashboards and insights help teams understand:
- System behaviour
- Incident trends
- Performance bottlenecks
How AIOps Works (Step-by-Step)
- Data Collection
Logs, metrics, events, and traces are continuously ingested. - Data Normalisation
Raw data is cleaned, enriched, and standardised. - Pattern Recognition
ML models identify normal behaviour patterns. - Anomaly Detection
Deviations from baseline behaviour are detected in real time. - Event Correlation
Related alerts are grouped into a single incident. - Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
AI identifies the most probable cause of failure. - Prediction & Prevention
Models forecast future incidents based on trends. - Automated Response
Predefined or learned actions are triggered automatically.
Key Use Cases of AIOps
1. Intelligent Alert Management
- Reduces alert storms
- Eliminates duplicate alerts
- Prioritises incidents based on impact
2. Anomaly Detection
- Detects abnormal latency, CPU usage, and memory leaks
- Identifies performance degradation early
3. Root Cause Analysis
- Correlates signals across infrastructure, applications, and networks
- Pinpoints the exact source of failure
4. Predictive Analytics
- Forecasts capacity issues
- Predicts outages before they occur
5. Automated Incident Response
- Auto-remediation workflows
- Faster resolution with minimal human intervention
6. Change Impact Analysis
- Assesses risk of deployments
- Detects anomalies caused by recent changes
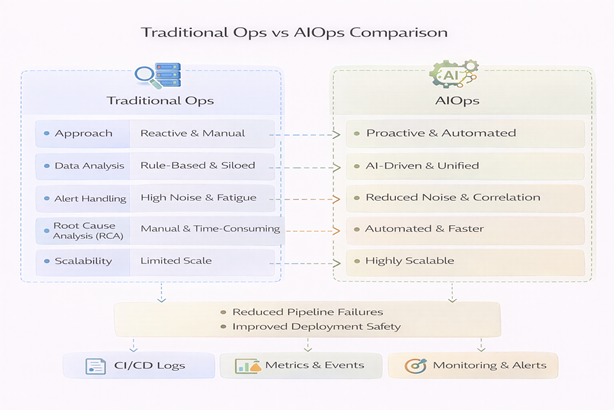
AIOps vs Traditional Monitoring
| Aspect | Traditional Monitoring | AIOps |
| Approach | Reactive | Proactive & Predictive |
| Alerts | Rule-based | Intelligent & correlated |
| Noise | High | Low |
| RCA | Manual | Automated |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| MTTR | High | Significantly reduced |
AIOps in DevOps and SRE
AIOps complements DevOps and SRE by:
- Improving reliability
- Reducing operational toil
- Enhancing deployment safety
- Supporting SLOs and SLIs
DevOps + AIOps
- Detect faulty deployments early
- Enable automated rollbacks
- Improve CI/CD feedback loops
SRE + AIOps
- Supports error budget management
- Improves incident response
- Enhances service reliability
Popular AIOps Tools and Platforms
Commercial Tools
- Splunk ITSI
- Dynatrace Davis AI
- Moogsoft
- IBM Watson AIOps
- Datadog Watchdog
- New Relic Applied Intelligence
Open-Source & Ecosystem Tools
- Prometheus + ML integrations
- ELK Stack with ML plugins
- OpenTelemetry
- Kubeflow (for ML pipelines)
Benefits of AIOps
- Faster incident detection and resolution
- Reduced operational costs
- Improved system reliability
- Better user experience
- Scalable operations
- Reduced human error
- Proactive problem prevention
Challenges and Limitations of AIOps
- High-quality data requirements
- Initial setup complexity
- Model training and tuning
- Integration with existing tools
- Trust in automated decisions
- Skill gaps in AI/ML understanding
Best Practices for Implementing AIOps
- Start with clear use cases
- Integrate with existing monitoring tools
- Clean and normalise data
- Start small and scale gradually
- Combine human expertise with automation
- Continuously retrain ML models
- Measure success using KPIs like MTTR
Future of AIOps
The future of AIOps includes:
- Self-healing systems
- Autonomous operations
- Deeper integration with GitOps
- AI-driven capacity planning
- Real-time business impact analysis
AIOps is evolving from assisted intelligence to autonomous intelligence.
FAQs – AIOps
1. Is AIOps only for large enterprises?
No. While large enterprises benefit greatly, mid-sized organisations can also adopt AIOps gradually.
2. Does AIOps replace DevOps or SRE?
No. AIOps enhances DevOps and SRE by automating analysis and reducing manual effort.
3. Is AIOps fully autonomous?
Most platforms are semi-autonomous today, with humans still in the loop.
4. What data is required for AIOps?
Logs, metrics, traces, events, and historical incident data.
5. Can AIOps prevent outages?
Yes, through predictive analytics and proactive remediation.
6. Is AIOps expensive?
Costs vary. Open-source and hybrid approaches can reduce expenses.

